How Your Brain Processes Information
- Genetically determined circuits are the foundation of the nervous system.
- Neuronal circuits are formed by genetic programs during embryonic development and modified through interactions with the internal and external environment.
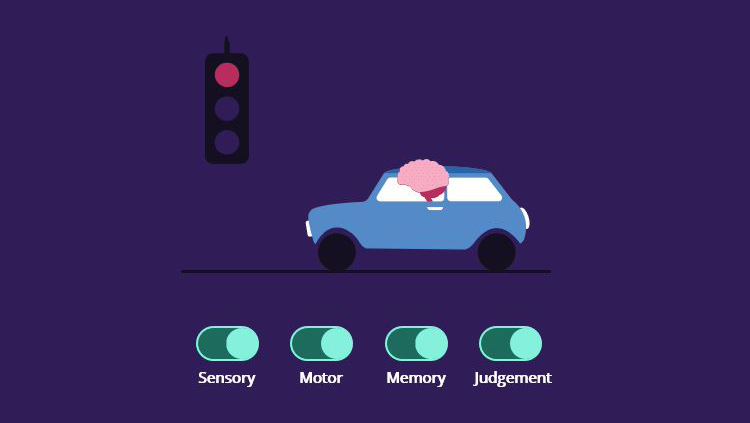
- Sensory circuits (sight, touch, hearing, smell, taste) bring information to the nervous system, whereas motor circuits send information to muscles and glands.
- The simplest circuit is a reflex, in which sensory stimulus directly triggers an immediate motor response.
- Complex responses occur when the brain integrates information from many brain circuits to generate a response.
- Simple and complex interactions among neurons take place on time scales ranging from milliseconds to months.
- The brain is organized to recognize sensations, initiate behaviors, and store and access memories that can last a lifetime.