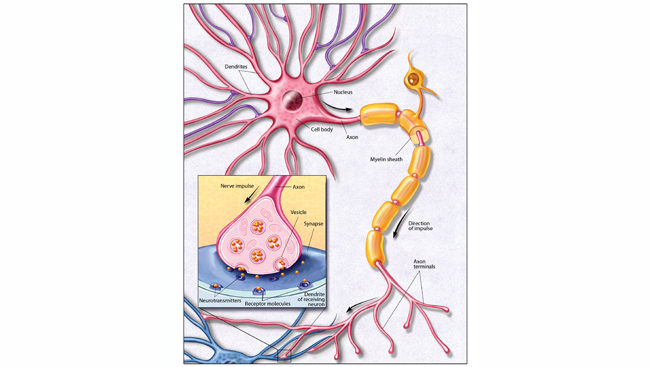
Receiving Information: Receptors and Molecular Signaling
- Reviewed30 Nov 2022
- Author Diane A. Kelly
- Source BrainFacts/SfN
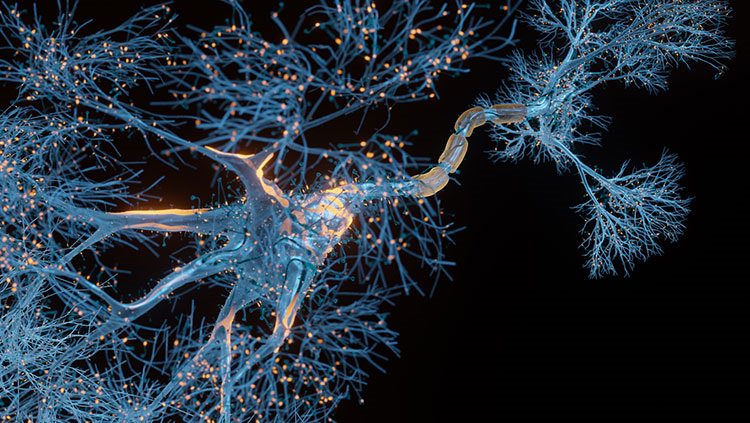
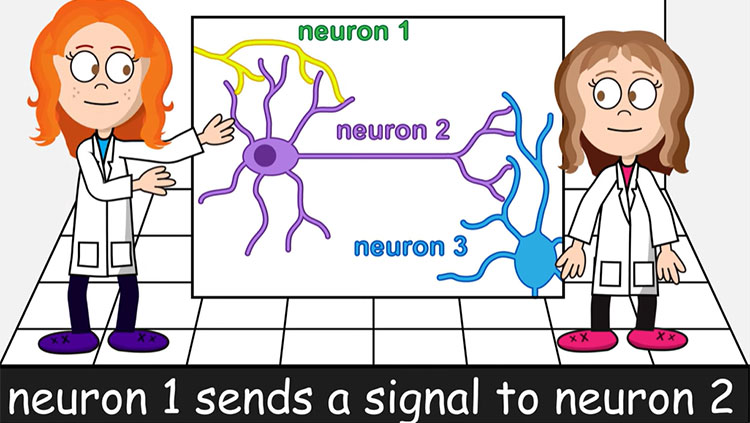
Neurons have receptors for many molecules that can change the way they function. These molecules include hormones, which send the brain specific cues about the condition and activity of distant tissues in the body; neuromodulators such as the endocannabinoids, cannabis-like chemicals that seem to suppress neurotransmitter release; and prostaglandins, small lipids that change the brain’s response (increasing pain sensitivity) to pain and inflammation.
Individual neurons have receptors for different subsets of hormones and neuromodulators. In each case, these molecules are signals that trigger a series of chemical reactions inside the cell. The process starts when one of these molecules binds to its specific receptor. If the receptor is on the surface of the cell, the bound molecule changes the receptor’s shape across the cell membrane and starts a chain of intracellular reactions. This signal transduction pathway ultimately modifies neuronal function, either by shifting the cell’s ion balance or by changing the activity of specific enzymes.
If a molecule can diffuse through the cell membrane — as occurs with steroid hormones like estradiol or cortisol — its receptor might be a protein inside the neuron’s soma. When the hormone binds to its receptor, the complex can transform into a transcription factor that is capable of entering the cell nucleus, binding to specific genes and changing their activity.
Adapted from the 8th edition of Brain Facts by Diane A. Kelly.
CONTENT PROVIDED BY
BrainFacts/SfN
References
Albuixech-Crespo, B., López-Blanch, L., Burguera, D., Maeso, I., Sánchez-Arrones, L., et al. (2017). Molecular regionalization of the developing amphioxus neural tube challenges major partitions of the vertebrate brain. PLOS Biology, 15(4): e2001573. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.2001573
Barton, R. A., & Venditti, C. (2014). Rapid Evolution of the Cerebellum in Humans and Other Great Apes. Current Biology, 24(20), 2440–2444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2014.08.056
Bekkers, J. M. (2011). Pyramidal neurons. Current Biology, 21(24), PR975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2011.10.037
Belkhiria, C., Driss, T., Habas, C., Jaafar, H., Guillevin, R., & de Marco, G. (2017). Exploration and Identification of Cortico-Cerebellar-Brainstem Closed Loop During a Motivational-Motor Task: an fMRI Study. The Cerebellum, 16, 326–339. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12311-016-0801-1
Bromfield, E. B., Cavazos, J. E., Sirven, J. I. (2006). An Introduction to Epilepsy, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK2508/
Carpenter, R., & Reddi, B. (2012). Neurophysiology: A Conceptual Approach, 5th edition. Hodder Arnold: London.
Castro, A., Becerra, M., Manso, M. J., & Anadón, R. (2015). Neuronal organization of the brain in the adult amphioxus (Branchiostoma lanceolatum): A study with acetylated tubulin immunohistochemistry. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 523(15), 2211–2232. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.23785
Clarke, L. E., & Barres, B. A. (2013). Emerging roles of astrocytes in neural circuit development. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 14, 311–321. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn3484
Fain, G. L., & O’Dell T. J. (2014). Molecular and Cellular Physiology of Neurons, 2nd edition. Harvard University Press: Cambridge.
Forger, N. G. (2016). Epigenetic mechanisms in sexual differentiation of the brain and behaviour. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 371(1688), 20150114. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2015.0114
Frohlich, F. (2016). Network Neuroscience, 1st edition. Academic Press: London.
Guo, J. U., Ma, D. K., Mo, H., Ball, M. P., Jang, M. H., Bonaguidi, M. A., Balazer, J. A., Eaves, H. L., Xie, B., Ford, E., Zhang, K., Ming, G. L., Gao, Y., & Song, H. (2011). Neuronal activity modifies the DNA methylation landscape in the adult brain. Nature Neuroscience, 14, 1345–1351. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2900
Hammond, C. (2014). Cellular and Molecular Neurophysiology, 4th edition. Academic Press.
Human Brain. (2017). Allen Brain Atlas. Allen Institute for Brain Science. https://human.brain-map.org/
Lee, A., Fakler, B., Kaczmarek, L. K., & Isom, L. L. (2014). More Than a Pore: Ion Channel Signaling Complexes. The Journal of Neuroscience, 34(46), 15159–15169. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3275-14.2014
Noback, C. R. et al (eds.). (2005). The Human Nervous System: Structure and Function, 6th edition. Humana Press: Totowa NJ.
O'Muircheartaigh, J., Keller, S. S., Barker, G. J., & Richardson, M. P. (2015). White Matter Connectivity of the Thalamus Delineates the Functional Architecture of Competing Thalamocortical Systems. Cerebral Cortex, 25(11), 4477–4489. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhv063
Peer, M., Nitzan, M., Bick, A. S., Levin, N., & Arzy, S. (2017). Evidence for Functional Networks within the Human Brain's White Matter. The Journal of Neuroscience, 37(27), 6394–6407. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3872-16.2017
Pyka, M., & Cheng, S. (2014). Pattern Association and Consolidation Emerges from Connectivity Properties between Cortex and Hippocampus. PLOS ONE, 9(1), e85016. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0085016
Saladin, K. (2015). Anatomy & Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function, 7th edition. McGraw Hill: New York.
Schneider, G. E. (2014). Brain Structure and its Origins: in Development and in Evolution of Behavior and the Mind. MIT Press: Cambridge.
Sheng, M., Kim, E. (2011). The postsynaptic organization of synapses. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, 3(12), a005678. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22046028
Sporns, O. (2013). Structure and function of complex brain networks. Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience, 15(3), 247–262. https://doi.org/10.31887/DCNS.2013.15.3/osporns
Verberne, A. J., Sabetghadam, A., & Korim, W. S. (2014). Neural pathways that control the glucose counterregulatory response. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 8(38). https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2014.00038
Wells, R. B. (2005). Cortical Neurons and Circuits: A Tutorial Introduction. https://webpages.uidaho.edu/rwells/techdocs/Cortical%20Neurons%20and%20Circuits.pdf